Offering high levels of load, speed and duty cycles, Roller Screw & Nut combinations can provide designers a long-lived and accurate solution for linear motion. They provide high axial rigidity, positioning accuracy, mechanical repeat-ability and low sensitivity to contamination. Commonly used in everything from artificial hearts to satellites, roller screws can also be found in radar arrays, optical equipment, transportation, measuring equipment and much more.
Knowing the basics of their anatomy and specifications can help you determine if roller screws are the right solution for you.
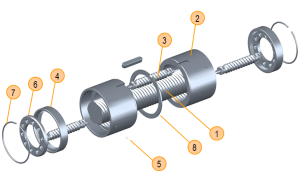
Anatomy
- Screw Shaft
- Nut
- Planetary Roller
- Ring Gear
- Pin
- Spacer Ring
- Spring Ring
- Calibrated Spacer
Specifications
Diameters – 8 to 75mm (.31 to 2.95″)
Leads – 2 to 42mm (.079 to 1.65″)
Precision Lead accuracy – IOS 5 (standard) ISO 3 & ISO 1
Materials – Medium carbon induction hardened alloy steel screws and High Grade bearing steel rollers should be specified
Nut Styles – Split or one-piece solid nuts in a cylindrical or flanged style